Polar Vortex Collapse Forecast 2025. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. […]
Polar Vortex Collapse Forecast 2025. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the.
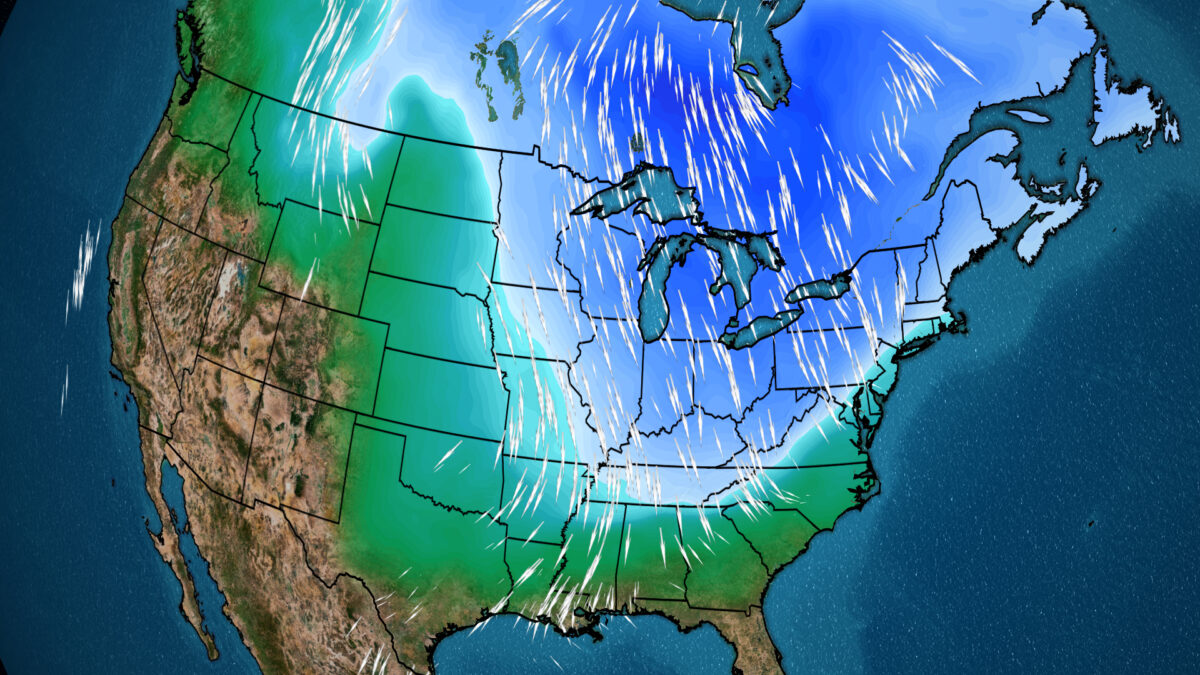
By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. This upcoming event in the stratosphere looks stronger than the first one and is forecast to be the final collapse of the polar.








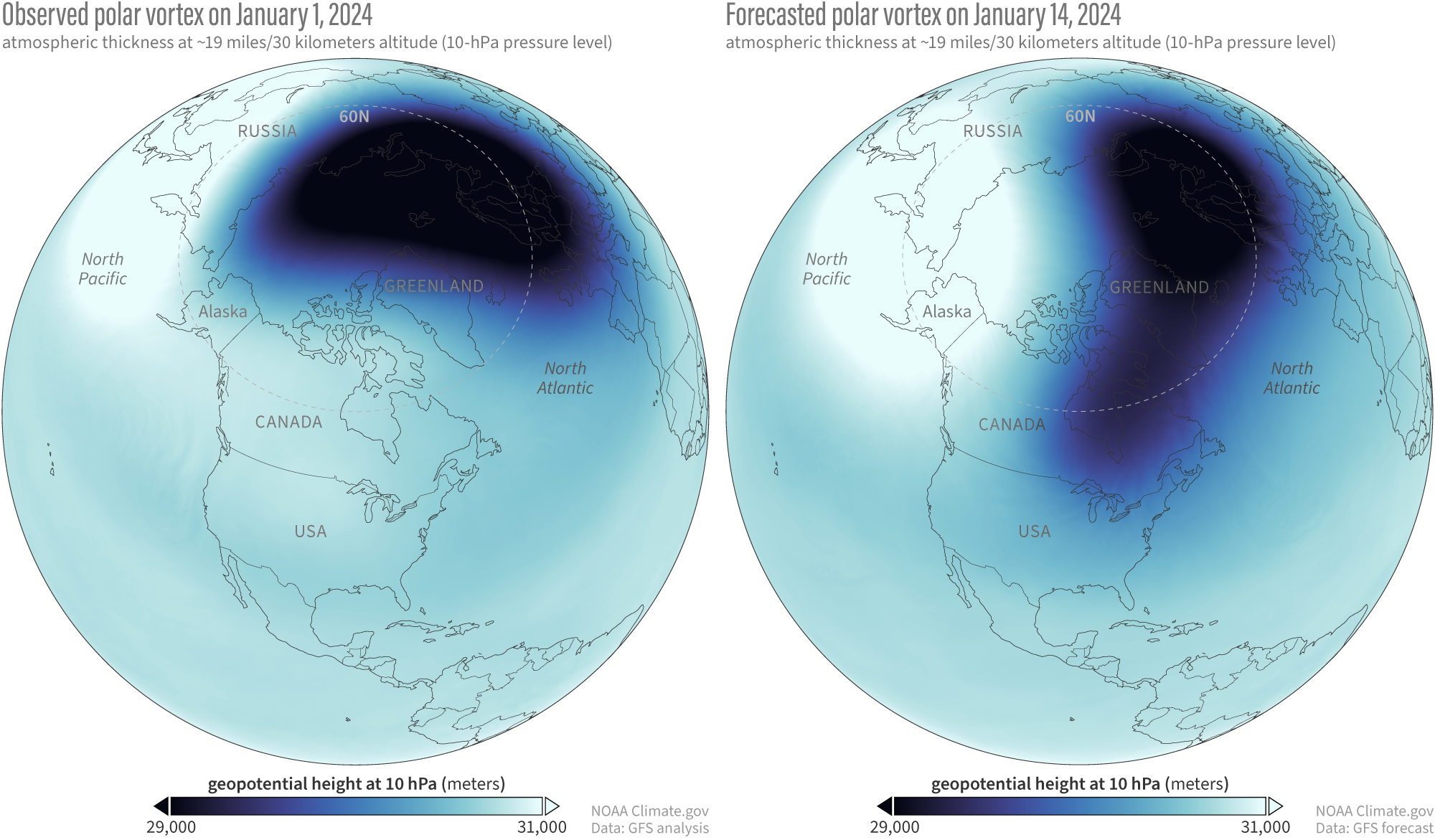

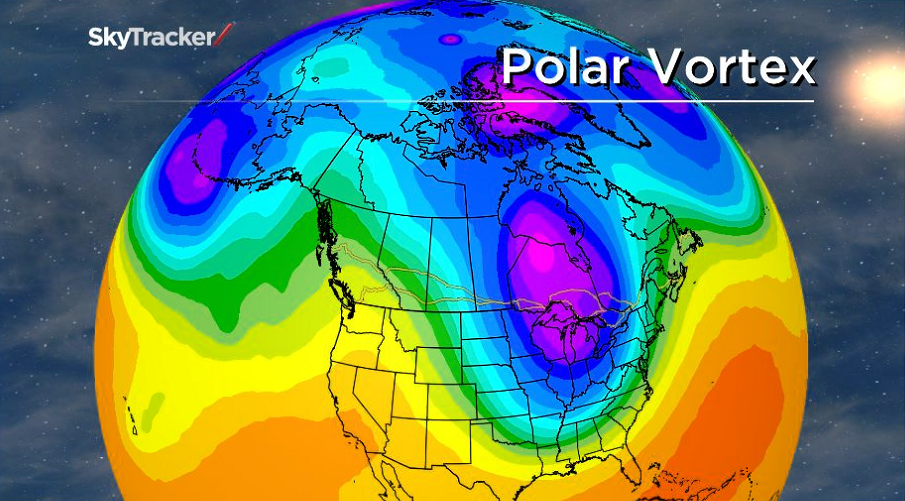

The Forecast Line Shows No Cooling Back, Which Is A Sign That The Polar Vortex Will Not Recover And Will Not Return In Any Proper Form Until The Next Winter Season Of 2025/2026.
Current forecasts, grounded in climate models and atmospheric analysis, point to significant stratospheric warming in march. By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. Arctic ice recovered more slowly than usual in december and january, likely due to polar vortex pulling freezing air from the arctic.
If Strong Enough, This Event Can Collapse The Polar Vortex Circulation, Impacting The Weather Patterns Below For The Weeks Ahead.
By march 10, 2025 (middle panel), the gfs forecast indicates the polar vortex will be nudged farther off the pole, with warmer air flooding the. This upcoming event in the stratosphere looks stronger than the first one and is forecast to be the final collapse of the polar.